| YFull: Tutorial |
What is YFull
YFull is a DNA analysis service that allows customers to analyze raw data files (BAM and CRAM) obtained from next-generation sequencing (NGS). It aims to study the origin in the direct paternal line (Y DNA or Y chromosome) and the direct maternal line (Mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). Interpretation using YFull’s proprietary software packages provides precise positioning of the sample on the human family tree (YTree and/or MTree), analysis of all known (named) single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and short tandem repeats (Y-STRs), and determination of novel ("private") SNPs.
The YFull database is constantly updated with new samples, currently totaling several tens of thousands. One part of the database contains raw data from various scientific publications collected around the world and ancient DNA samples (aDNA) from people of different eras and cultures up to 40 thousand years old. The other part of the database are samples from individuals whose Y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA were fully decoded with Whole Genome Sequencing or a targeted sequencing approach.
YTree (Y chromosomal Tree) and MTree (Mitochondrial Tree) are available for viewing to all researchers and visitors interested in genealogy. The YTree can be viewed in a "classic" tree view, as well as a "chart" or "scientific", and the "Live" tree shows changes in the structure online, such as adding or removing subclades. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms on the Y chromosome (Y-SNPs), which are passed from father to son through generations, as well as mutations in mtDNA inherited in a direct maternal line, allow you to trace the spread of mankind from today to tens and hundreds of thousands of years in the past. Our mythical ancestors are the so-called “Y chromosomal Adam” and “Mitochondrial Eve”, real people who lived at different times several hundred thousand years ago, but whose descendants survived and spread throughout the world. This fascinating journey to its origins is available to anyone who obtained their raw genomic data through Whole Genome Sequencing.
This YFull tutorial will follow the sections on the left-hand sidebar. The sidebar is divided into 5 main sections: SNPs, STRs, mtDNA, RAW data, and others. Individual reports in each section are described below and important features are labeled and explained under each example.
Y chromosome analysis
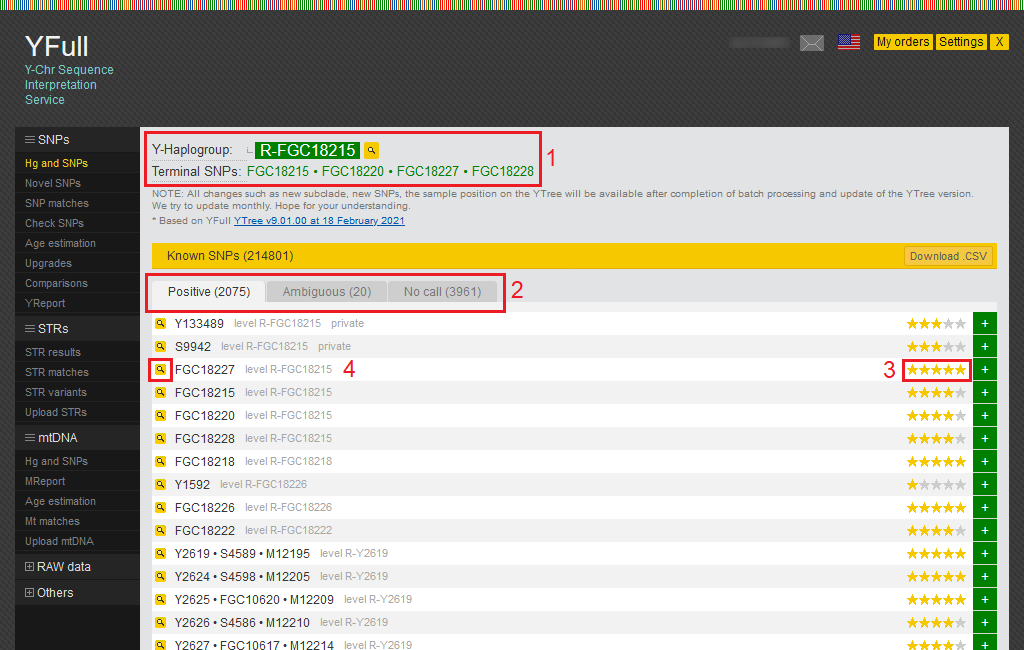
Hg and SNPs

1) This area displays your Y haplogroup and a link to YTree, as well as a list of terminal SNPs that are common to all samples belonging to your haplogroup.
2) The SNPs found in your sample are shown here and divided into three categories: Positive, Ambiguous, and No call. Positive SNPs are mutations that were found in your Y chromosome. Ambiguous SNPs we were not able to determine with certainty. You can download the entire list of SNPs in CSV format.
3) All SNPs in the YFull database are rated and marked with stars from 1 to 5. The rating is based on a set of criteria that assess SNP quality. When YTree building, SNPs with a 3-5 star rating are mainly used.
4) Detailed information about SNP can be obtained by clicking on the magnifying glass icon.
RAW Data
You can browse your raw data for specific SNPs of interest. This option is located on the left hand side bar under RAW data. The page can be used to check any SNP on the Y chromosome.
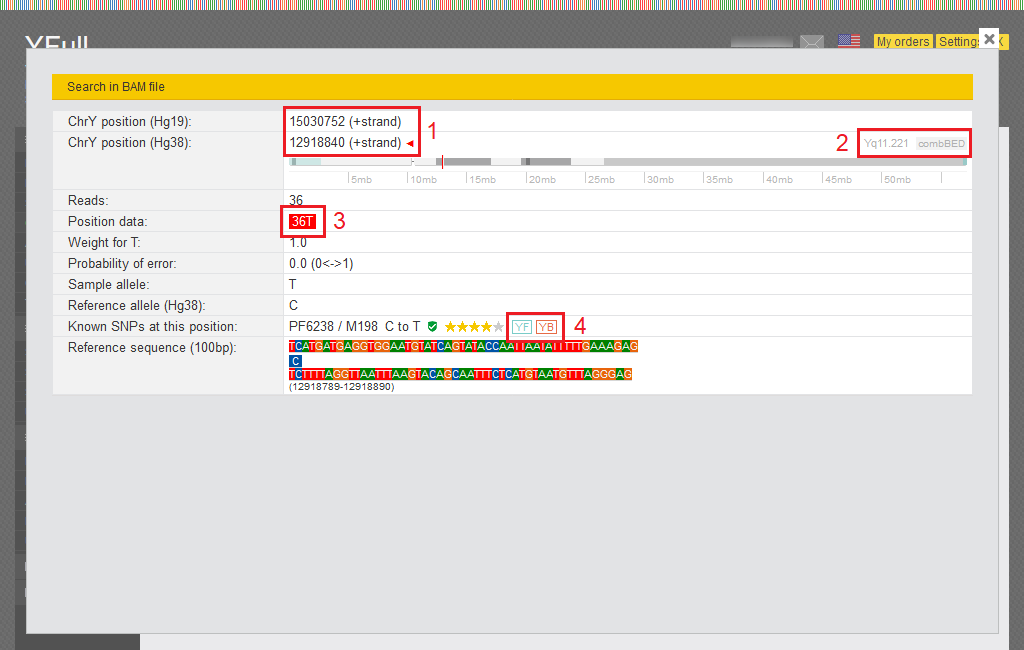
1) SNP position is indicated in the reference sequence Hg19 as well as Hg38
2) Information about the region of the Y chromosome where the SNP is located. The "combBED" icon, which means that this SNP is used for age estimation.
3) The number of sequencing reads in your data that cover this SNP.
4) The icons “YF” and “YB” mean that SNP information is available in the YFull database and on Ybrowse.org.
Novel SNPs
SNPs found on your Y chromosome that are currently not found in anyone else’s data in the YFull database are considered novel (“private”). A list of these options is presented in the report on the “Novel SNP” page.
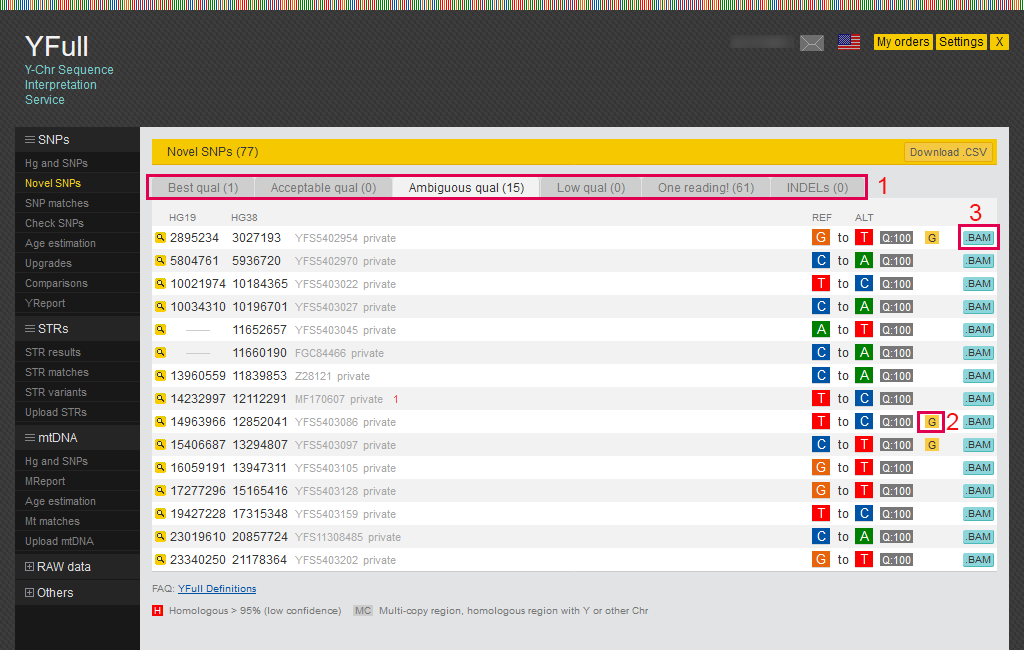
1) All “private” SNPs are divided into four categories based on sequencing quality and other criteria.
2) There may be several icons in the SNP line. “G” means that the SNP is near a gene. “H” means that the SNP is located in a homologous region, that is, one that is similar to other regions on the Y chromosome or on other chromosomes. “MC” means that the SNP is in a multicopy region, that is, in a region homologous to another region of the Y chromosome.
3) You can view the mapped sequence fragment (.bam) for the area around the SNP using the “BAM viewer”.
SNP matches
This report provides a list of samples with which there is an SNP match with your sample. At the time of this writing, the list is limited to an age range of 3,500 ybp (years before present). You can read more about the methodology behind SNP matching on our website.
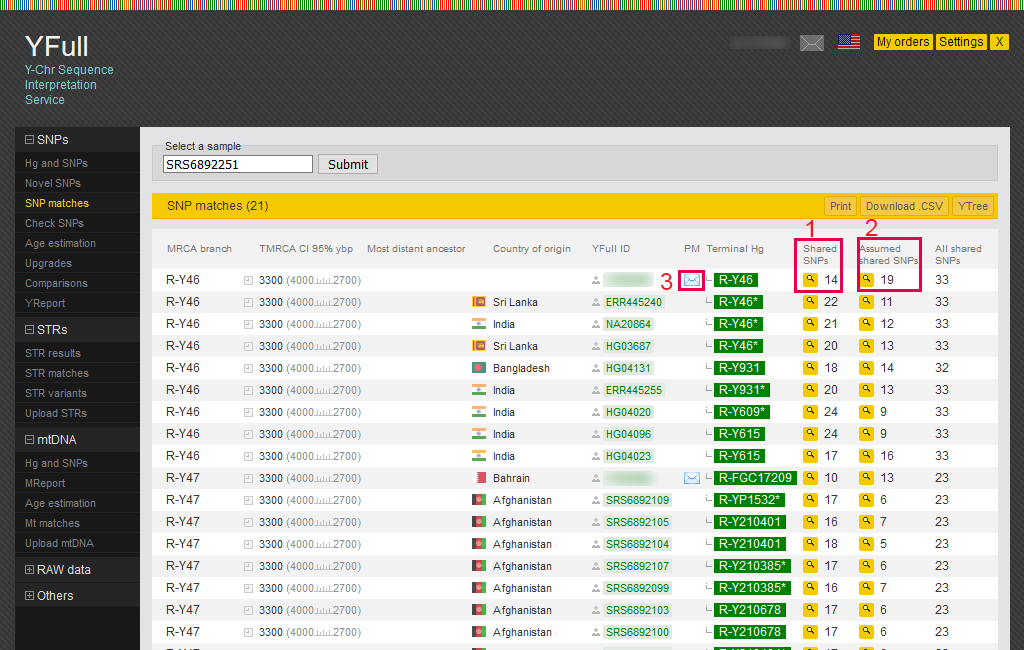
1) The number of common SNPs shared between your sample and another sample. SNPs can be viewed in the pop-up window.
2) Additional SNPs that are assumed to be shared between your sample and another sample.
3) Using this link, you can send a personal message to a YFull user.
STR results
Y-STRs are short tandem repeats of DNA fragments, for example, “GAAA/GAAA/GAAA/GAAA,” etc. They are used as genetic markers in population genetic studies for shorter time intervals due to their greater variability compared with SNPs.
At the moment, YFull is showing a report on 780 Y-STR markers. For each of the markers you can see the number of copies present on your Y chromosome. To extract Y-STR markers using software that developed by YFull and based on unique proprietary algorithms that can work with palindromic markers of varying complexity up to 4 copies inclusive.
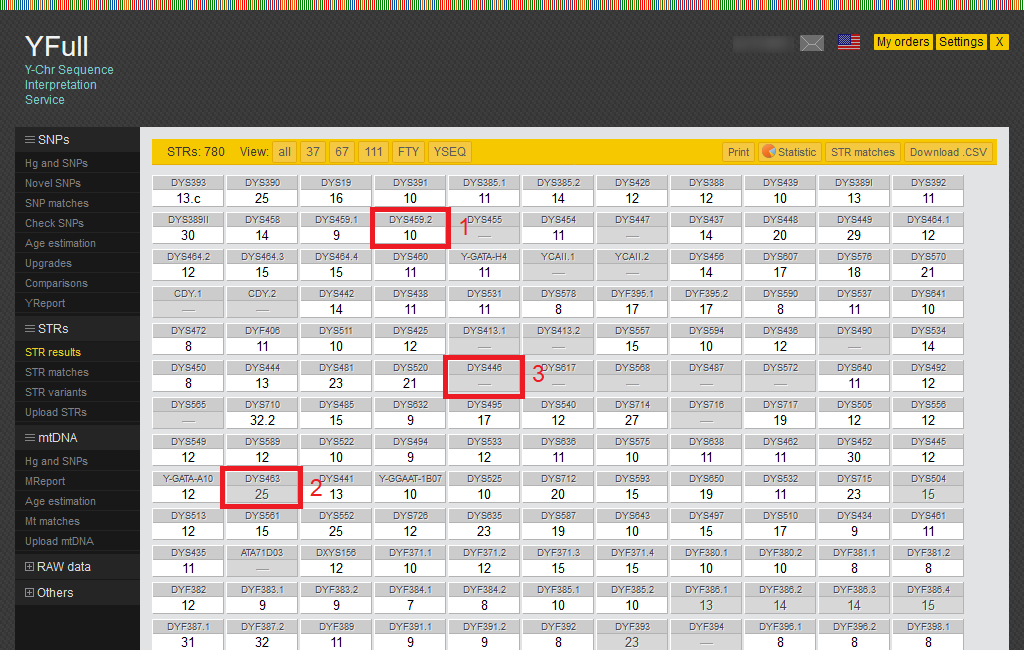
1) Counts of STR markers that are considered reliable are shown on a white background.
2) Counts of STR markers that are considered ambiguous are shown on a gray background.
3) Counts of STR markers that have not been determined or are considered unreliable is shown as a dash.
STR matches
The STR marker counts in your sample are compared to the counts in other samples. This enables us to find individuals who are your (distant) relatives on the paternal side. The counts of various STR markers are grouped into groups called haplotypes.
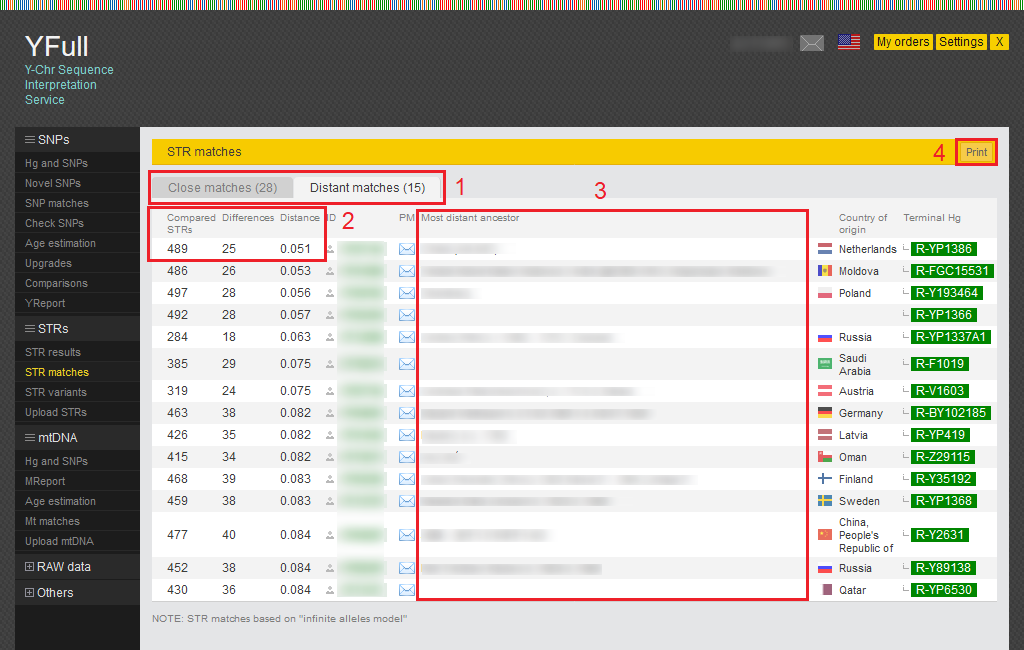
1) The table of STR matches is divided into two tabs: Close matches and Distant matches. Close matches with distance less than 0.050 and distant matches with distance from 0.050 to 0.085. You can read more about the STRs comparison methodology on our website.
2) These columns show the number of compared markers and the differences between your sample and other samples.
3) AAdditional information about the most distant paternal ancestor ("Settings" page > "Most distant ancestor").
4) Button for generating a printer-friendly page.
STR variants
This report includes a list of STR variants from your unique (“private”) mutations down the branches of the YTree to the root where the “Y Chromosomal Adam” is located.
Some slowly mutating STR markers are marked with 4 or 5 stars and can be added to YTree as they are the most stable and help in tree building.
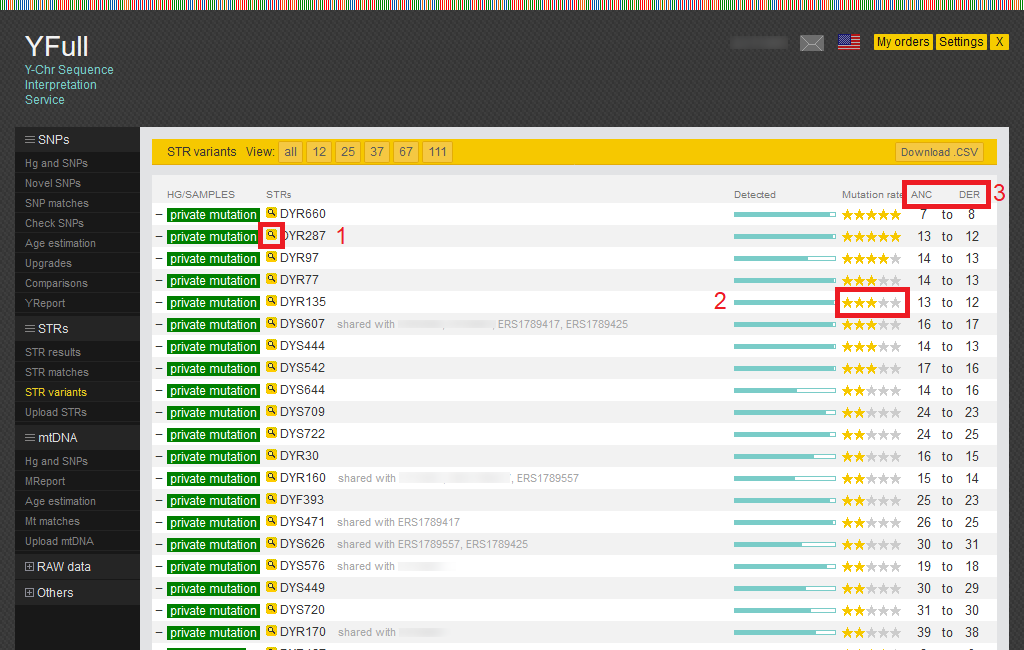
1) Detailed statistics for the STR marker can be viewed by clicking on the magnifying glass icon.
2) STR markers, like SNP markers, have a rating indicated by stars from 1 to 5, where 5 stars mean slowly mutating STR.
3) STR markers have ancestral (“ANC”) and derived (“DER”) alleles.
You can read more about STR variants methodology on our website.
Age estimation
The recalculation of the ages of all YTree subclades occurs at intervals of about 1-1.5 months. This is a time-consuming and resource-consuming procedure and therefore requires a certain amount of time. You can see the new YTree structure or a new subclade before the update is completed using the Live Tree. Age estimation is based on all samples with a “length coverage for age” of at least 5,927,015 base pairs.
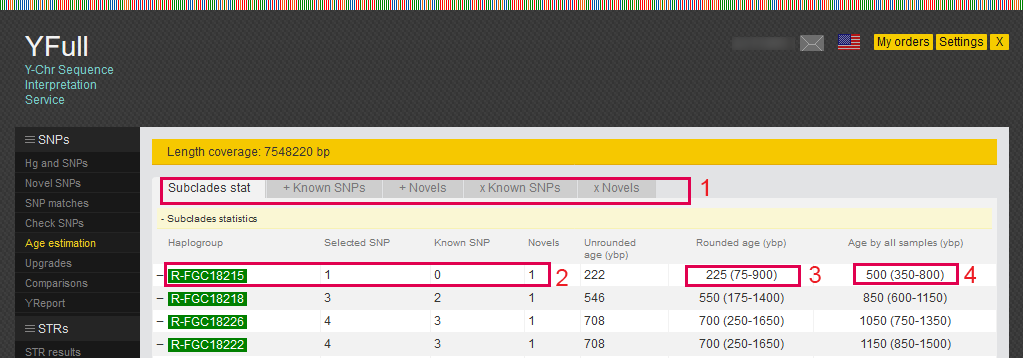
1) The report is presented in several tabs:
"Subclades statistics" - statistics of SNPs used for age estimation;
"+Known SNPs" - known SNPs used to estimate age;
"+Novels" - novel SNPs used to estimate age;
"xKnown SNPs" - known SNPs excluded from the estimation of age and on what reasons;
"xNovels" - novel SNPs excluded from the age estimation and on what reasons;
2) For the terminal subclade, when estimating the age, only novel SNPs of samples are taken.
3) Subclade age, taking into account data only for the current sample
4) Subclade age, taking into account data for all samples.
You can read more about the age estimation methodology on our website.
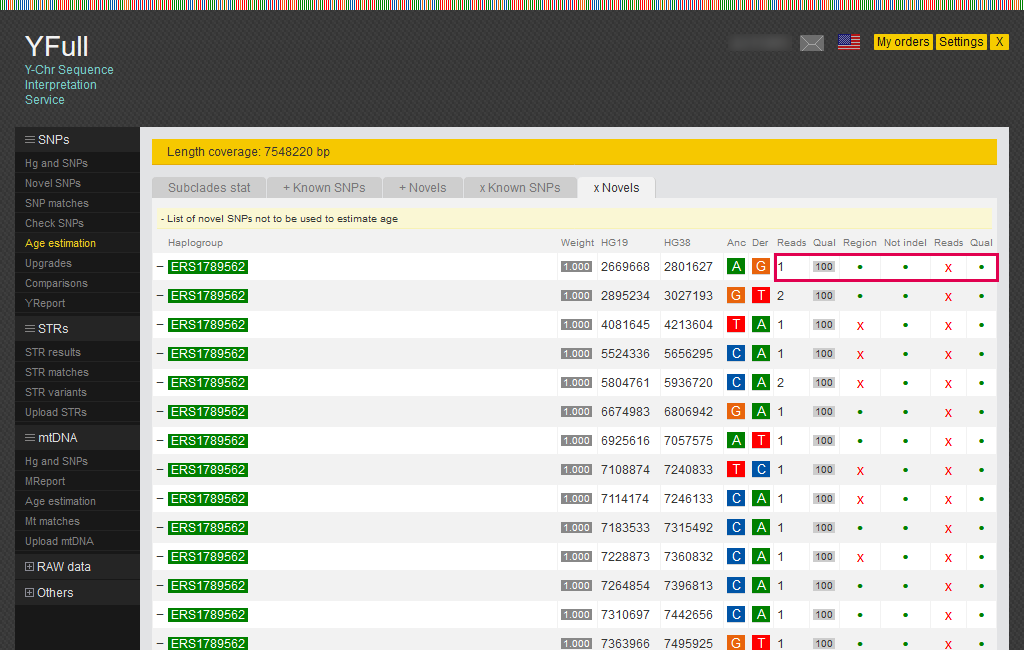
The “xNovels” tab shows the reasons why SNPs in the list were excluded from the estimation of age: SNP is outside the “combBED” region, deletion or insertion (InDel), low number reads, and insufficient SNP quality.
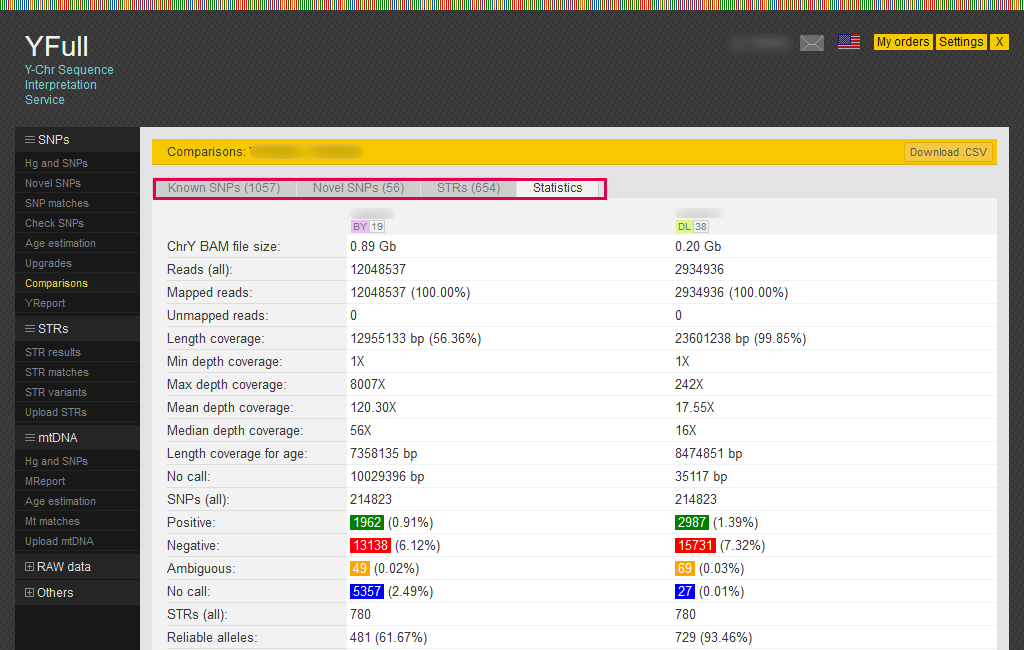
Comparisons
In YFull, in the presence of two or more sequences of the Y chromosome of one person obtained from different laboratories, it is possible to carry out a comparative analysis of the data by comparing them with each other. If only one sample is linked in the Personal Account, the tool will not be available. This report can be viewed on the "Comparisons" page. The report is conveniently divided into four tabs, where SNPs, STRs, and Statistics for different sequences are compared in detail.
Mitochondrial DNA analysis
The MTree is a tree of full mitochondrial sequencing (FMS). It contains several tens of thousands of scientific samples from Genbank as well as mitochondrial DNA data uploaded by individual users (excluding FTDNA and YSEQ). New branches are regularly added to the MTree. It currently has about 14 thousand branches. The MTree also has a large branch of Neanderthal and Denisovan paleo-DNA, as well as other ancient mitochondrial sequences.
Reverse mutations, which occur quite often, cause big problems in the construction of MTree. To this end, YFull is conducting additional research on the relationship between individual mito sequences. This is necessary to detect reverse mutations that might otherwise be missed by MTree's algorithms. Due to their high frequency of occurrence, some mutations are not used when building a MTree.
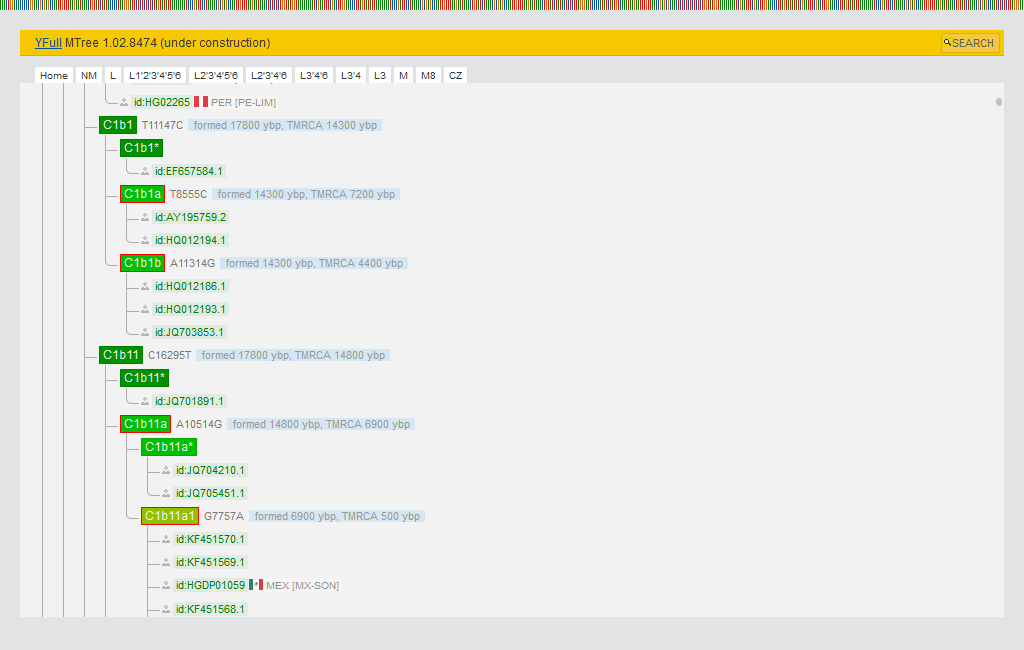
You can see your sample in the MTree and identify nearest relatives as well as distant ancestry. MTree subclades have their own confidence rating and are indicated by stars from 1 to 5. For convenience, they are highlighted in different colors on the tree. The rating is based on a set of criteria. For example, the 4-5 star rating corresponds to the subclades of the PhyloTree, or such subclades were formed by rare mutations.
All Mt reports use a comparison of a sample with two references: rCRS and RSRS. rCRS is an earlier Cambridge reference belonging to a European from haplogroup H2a2a1, and RSRS is a more modern reference, constructed the "Mitochondrial Eve" genome.
Hg and SNPs
All SNPs that we find in your mitochondrial DNA are shown in the report “Hg and SNPs.”
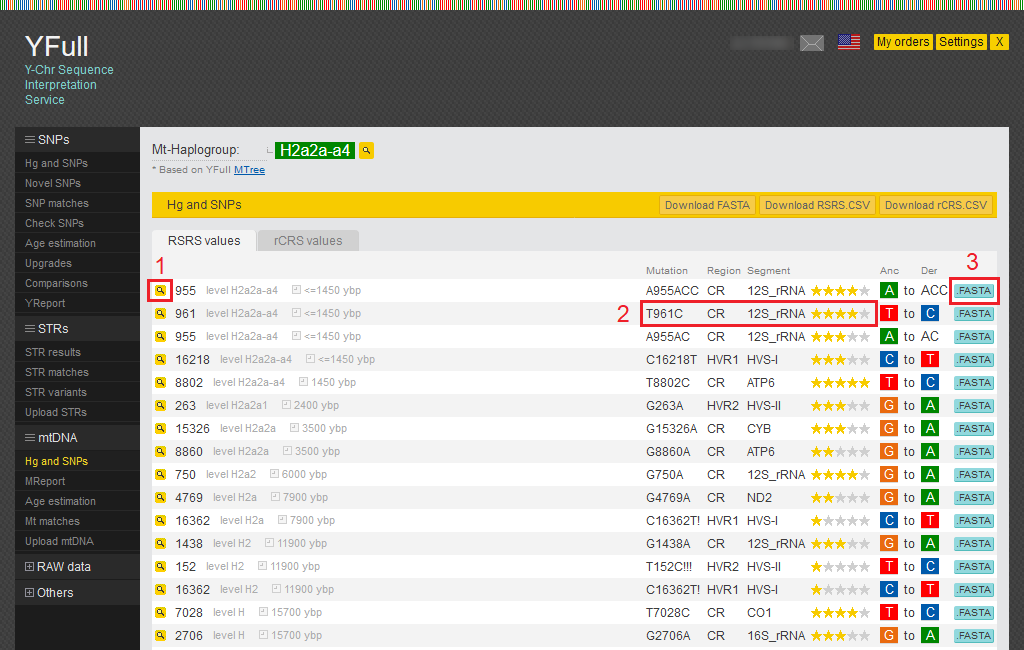
1) By clicking on the magnifying glass icon, you can view all known SNPs for that position.
2) Here you can see the mutation and its location in the mitochondrial DNA.
3) You can view the sequence of raw data by clicking on the “.FASTA” button.
Mt matches
Samples with SNPs that match the SNPs of your sample can be viewed in the “Mt matches” report.
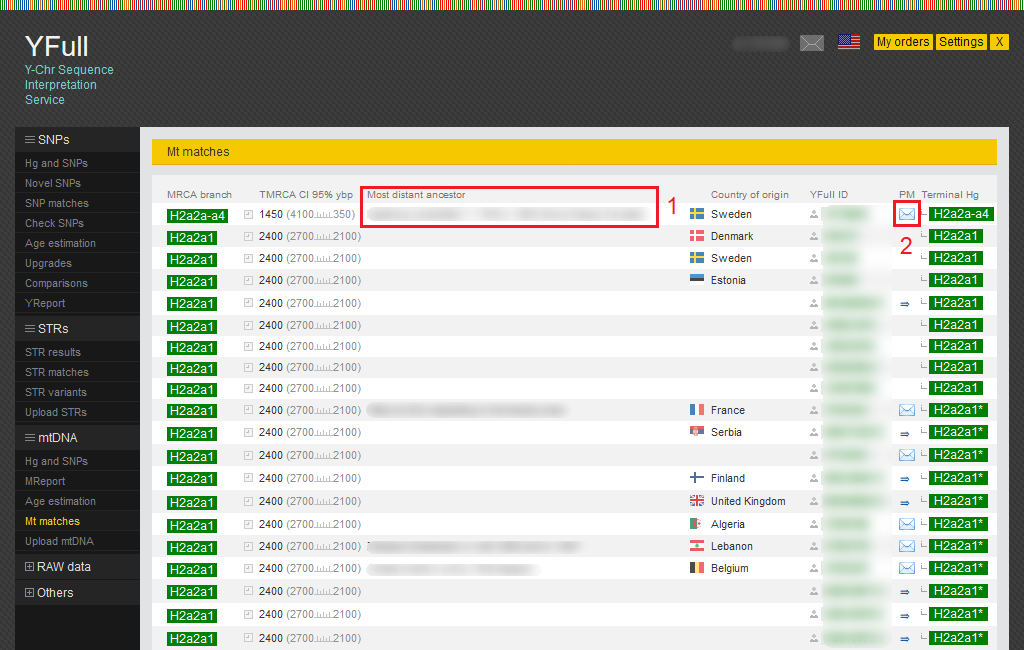
1) Additional information about the most distant ancestor (maternal line).
2) Using this link, you can send a personal message to a YFull user.
MReport
The main mitochondrial DNA interpretation report is the “MReport”, which lists all mutations in all mitochondrial DNA regions.
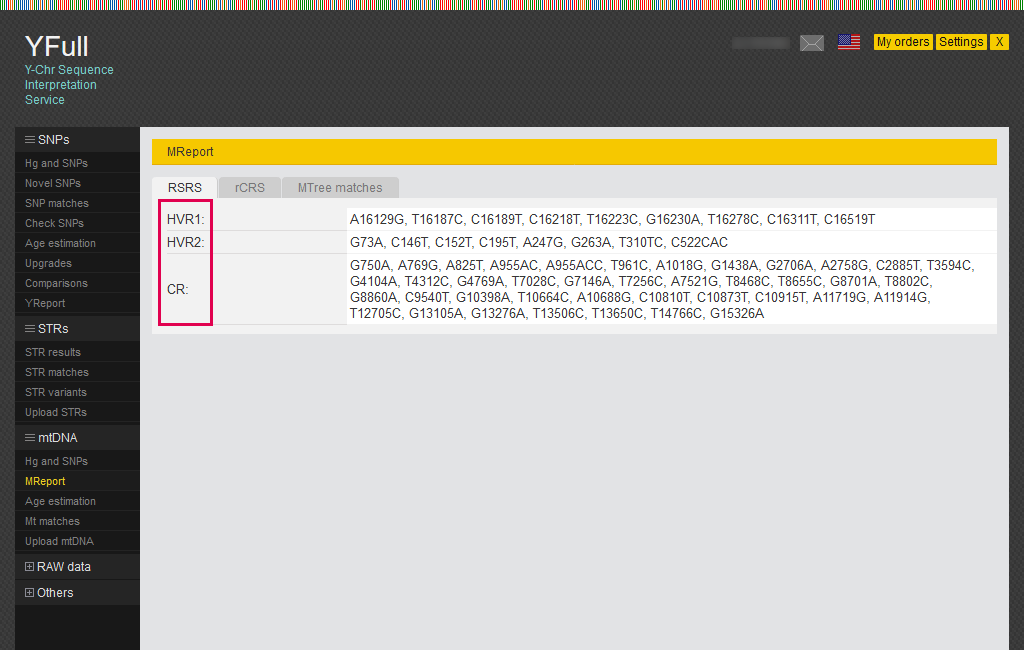
HVR1 (16024-16383) – hypervariable region No. 1 of mitochondrial DNA
HVR2 (57-574) – hypervariable region No. 2 of mitochondrial DNA
CR (575-16000) - coding region of mitochondrial DNA
On the “MTree matches” tab, all mutations are divided into groups. In particular, they include those that match other samples and those currently unique.
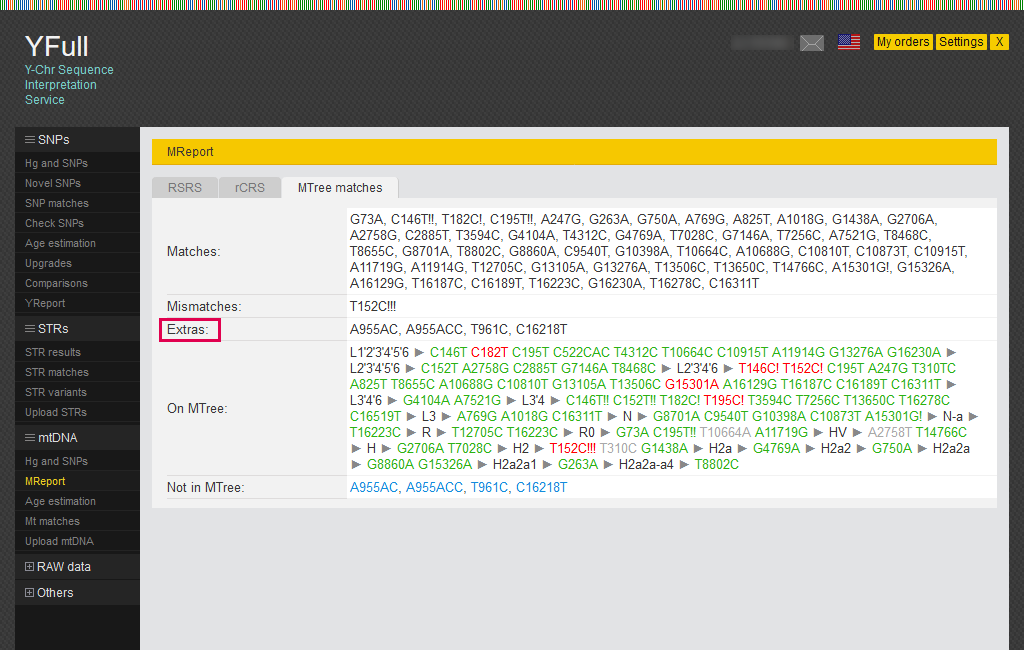
“Extras” are novel mutations found in your sample, that have not yet been added to the MTree.
Groups
A user of the YFull service can join a group (by haplogroup, by country, by region, by last name, etc.) to compare their results with other members of the group. The groups are divided into Y and Mt. The link to the list of groups is in the “Other” section of the main menu.
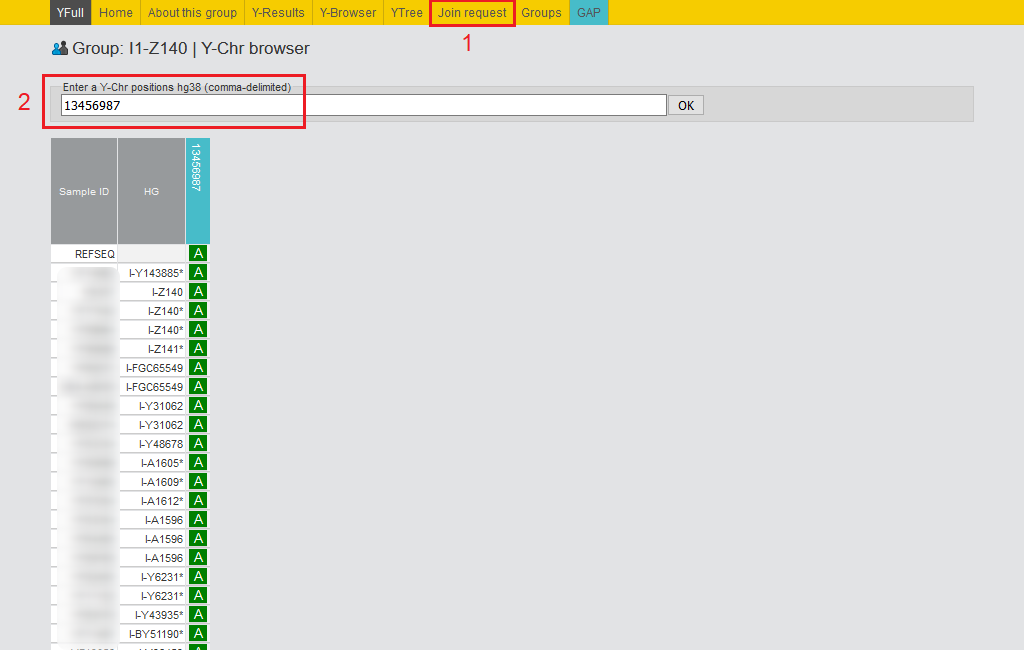
1) You can join a group by clicking on the “Join request” button in the selected group page’s horizontal menu. By joining a group, the user shares the results with other group members and can view the results of other group members (SNPs, STRs, etc.). You can contact another member by writing a private message. To leave a group at any time from the “Settings” page.
2) From the “Y-Browser” page, any group member can view any position of the Y chromosome for the entire group. The “Y-Results -> View Y-SNPs” page allows you to check the value of SNPs in all samples of a group by entering the name of SNPs separated by commas.
Similarly, on the “Y-Results -> View Y-STRs” page, you can STRs of the entire group.
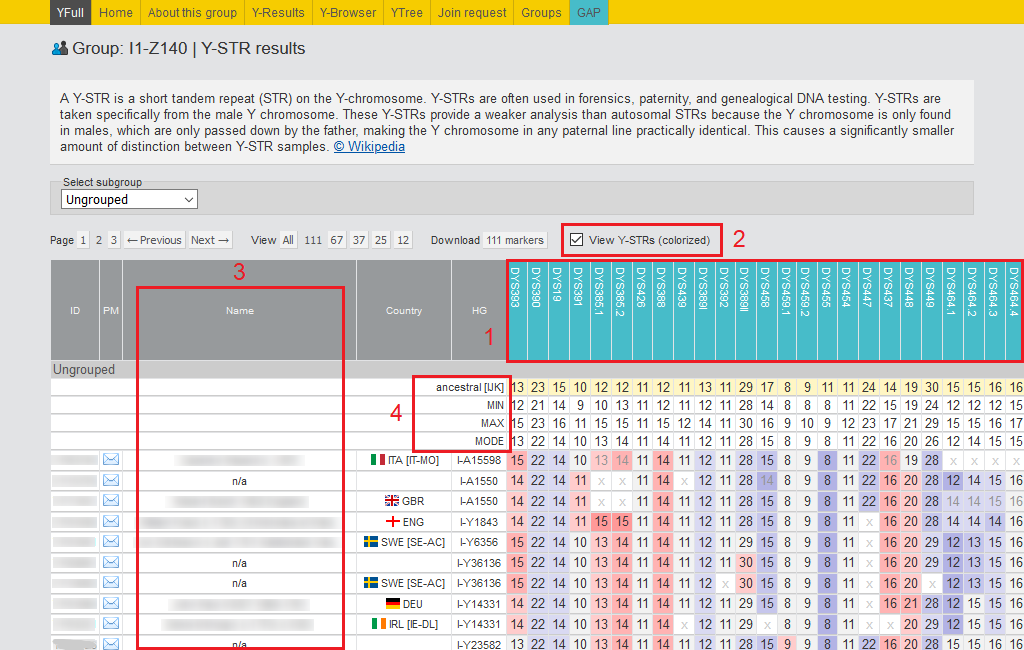
1) In the header, the names of the markers are listed. In the menu above, you can select the desired number of markers to view: 12, 37, 67, 111, or all.
2) With this tool, you can see the 780 STRs counts for all group members. The data looks much clearer showing the differences in the STRs values in a certain range with different background colors.
3) This column of the table displays information about the most distant direct ancestor (paternal line).
4) Consensus haplotypes for the maximum alleles, minimum alleles, and the reconstructed ancestral haplotype for the selected haplotypes group are displayed here. These tools help researchers explore haplogroups and individual subclades more deeply.
Mt groups are very similar in structure to Y groups..
Updating Trees
YTree is updated every 1-1.5 months. Each tree release has its unique number and date (YTree v9.01.00 from 18 February 2021). The list of YTree releases is published on the “Archive” page. You can follow the tree's development by selecting any update by clicking on the link with the version number.
The recalculation of the ages of all YTree subclades occurs every time the tree is updated. This is a time-consuming and resource-consuming procedure and therefore requires a certain amount of time. The estimation of the ages for the samples added after the YTree update is carried over to the trees next release.
MTree is updated in real-time as new samples and subclades are added. Within a month after adding a sample to MTree and YTree, the "new" flag appears next to the sample ID.
Privacy
YFull adheres to a strict security and privacy policy and does not share user data with third parties. Partial access only to certain interpretation results (for example, STR haplotypes, SNP data, etc.) can be given to group administrators and group members to which the user has joined. Joining the group, the user agrees to the terms and conditions and can also leave the group at any time. None of the users sees either the name or the email, and you can contact them by writing a private message inside the service.
Almost all information is depersonalized, and on the "Settings" page, you can change the privacy level for groups and for YTree / MTree. Optionally, you can add your sample anonymously using a pseudonym and a specially created email address. At the same time, you can, on the contrary, share your results with another user.
At any time, the user can delete his sample or account with all the data beyond recovery.
P.S.
This is not a detailed tutorial, but we wanted to describe only the main reports and tools of the YFull service compactly and understandably. The main purpose of interpretation is to provide absolutely all the information stored in the Y chromosome and Mitochondrial DNA raw data files. That can be extracted using YFull tools for a deeper study of the origin of their ancestors. Various tools are being improved, new samples, both scientific and ancient, are regularly added. Step by step, we together reconstruct the amazing history of our distant ancestors.
You can also read more information on the FAQ page
Edited by Christina Swords, Ph.D.